
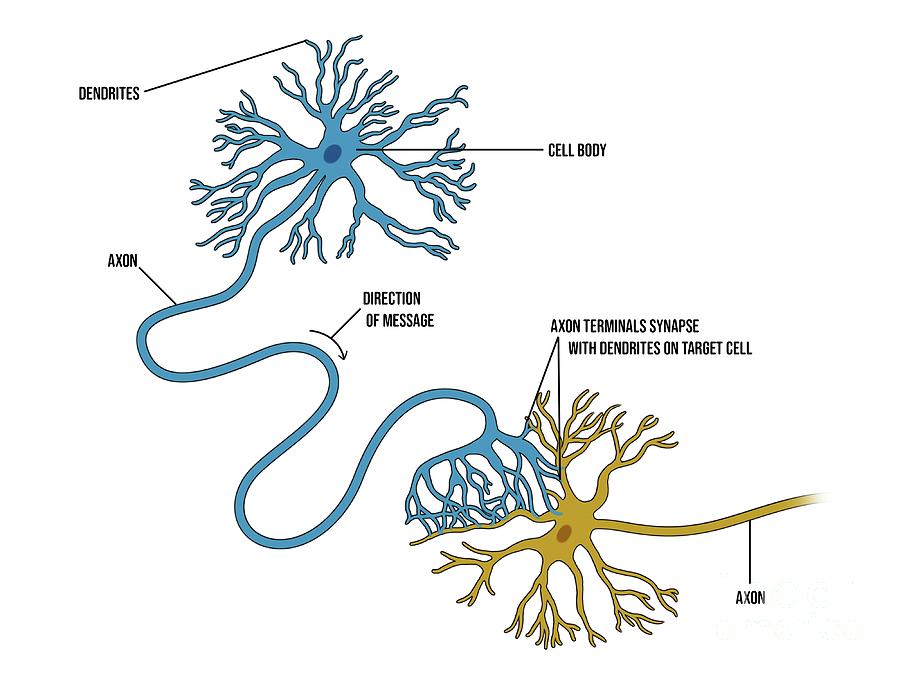
Upon cell cycle exit through asymmetric cell division (D2), the post-mitotic neuron (blue) goes through a multipolar transition where multiple neurites emerges rapidly from the cell body (D3) before one major process forms in the radial direction (D4) and becomes the leading process (LP). These cells have a long basal (radial) process attached to the basal membrane at the pial surface and a short apical process on the ventricle side (D1 see detail in Figure 5). Neurons are generated between E11 and E17 by radial glial progenitors in the ventricular zone of the mouse neocortex. ( D) Polarization of radially migrating pyramidal neurons in the mammalian neocortex. The trailing processes form a characteristic T-shaped axon (red in C6) whereas the leading process gives rise to the dendritic domain. Another process emerges from the cell body in the tangential direction (C4) and becomes the leading process, leading its migration towards the inner granule layer (IGL C5). Granule cell progenitors divide rapidly in the external plexiform layer (EGL C1) and upon cell cycle exit start adopt a bipolar morphology (C2) before migrating tangentially with a leading and a trailing process (C3). ( C) Polarization of granule cells in the mammalian cerebellum. The axon emerges from the basal process (red) and the dendrite emerges from the apical process (B4). Neuroepithelial progenitors (B1) transform into bipolar cells by first losing their basal attachment which starts branching in the inner plexiform layer (IPL) while the apical process starts branching in the prospective outer plexiform layer (OPL) before (B2) losing its apical attachment (B3). ( B) Polarization of mouse bipolar cells in the mouse retina. The axon (red) therefore emerges from the basal process and the dendrite emerges from the apical process (A6).
Upon cell cycle exit, the nucleus undergoes basal translocation (A4) and specifically loses its apical attachment while its basal process starts growing along the basal membrane (A5). Neuroepithelial progenitors characterized by an apical and a basal attachment undergo asymmetrical cell division at the apical surface (A1-A3).

( A) In vivo polarization of retinal ganglion cells in zebrafish ( Danio rerio) and mouse ( Mus musculus). Throughout these figures, the nascent axon is depicted in red and the somatodendritic domain in purple. Examples of the sequence of events leading to the polarized emergence of axon and dendrites in four distinct vertebrate neuronal cell types in vivo.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
